Venture Capital In the ever-evolving landscape of business and entrepreneurship (VC)
Emerges as a driving force behind the growth and success of innovative startups.
This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricate world of Venture Capital, exploring its origins, functions, impact, and the symbiotic relationship it fosters between investors and the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Options Trading: Concept Key, Types & Applications
Market capitalization weighted Complete Free Concept i
What is Equity? Concept, Types & Future Free Trends
Understanding the Genesis
It is a form of private equity financing that investors provide to startup and early-stage companies with high growth potential.
The objective is not only to fuel the growth of these companies but also to realize a substantial return on investment.
Venture capitalists, the entities or individuals providing this capital, play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of emerging businesses.
The Complete Financial Analyst Free Course
Building Responsive Websites: HTML And CSS Course
The Data Science Course:Data Science Bootcamp
Key Elements
- Risk and Reward: Involves a higher level of risk due to the early-stage nature of the investments. However, the potential rewards can be significant if the startup succeeds.
- Equity Stake: In exchange for funding, venture capitalists typically receive an equity stake in the startup. This means they become partial owners of the company.
- Active Involvement: Beyond providing capital, venture capitalists often offer strategic guidance, mentorship, and industry connections to help startups navigate challenges and scale.
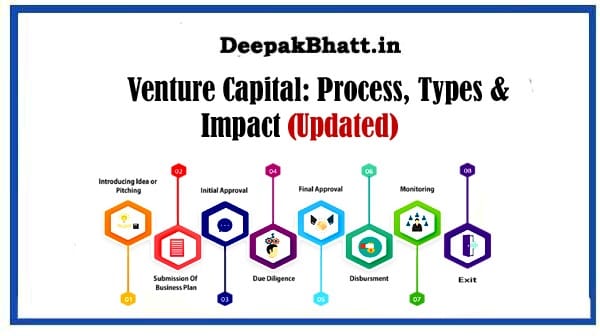
Process
Its operates through a structured process involving various stages, from initial investment to exit. Here’s an overview of the typical venture capital process:
1. Deal Sourcing:
Venture capitalists actively seek investment opportunities by scouting for promising startups. This process may involve networking, attending industry events, and collaborating with other players in the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
2. Due Diligence:
Once a potential investment is identified, thorough due diligence is conducted. This involves assessing the startup’s business model, market potential, team capabilities, and overall viability.
3. Term Sheet Negotiation:
If the due diligence phase is successful, the venture capitalist presents a term sheet outlining the proposed terms and conditions of the investment. This document is subject to negotiation between the investor and the startup.
4. Investment:
With agreed-upon terms, the venture capitalist invests. This infusion of capital is often done in rounds, with each round representing a new stage of funding as the startup progresses.
5. Post-Investment Involvement:
Venture capitalists don’t just provide funding and walk away. They actively engage with the startup, offering expertise, strategic advice, and networking opportunities to enhance the chances of success.
6. Scaling and Growth:
As the startup grows, additional funding rounds may be initiated to support scaling efforts. Venture capitalists may bring in additional investors during these rounds.
7. Exit Strategy:
The ultimate goal for both the startup and the venture capitalist is a successful exit. This can take the form of an Initial Public Offering (IPO), acquisition by a larger company, or other exit strategies that provide a return on investment.
Types
Its comes in various forms, each catering to different stages of a startup’s development. Here are the main types:
1. Seed Capital:
Seed capital is provided at the earliest stages of a startup’s life. It helps founders take their initial idea or prototype and develop it into a viable business.
2. Early-Stage:
Early-stage venture capital is directed toward startups that have a proven concept and are in the early stages of product development or market entry.
3. Expansion or Growth Capital:
Expansion or growth capital is injected into startups that have achieved a level of success and are looking to scale their operations, enter new markets, or enhance their product offerings.
4. Late-Stage:
Late-stage venture capital is provided to well-established startups that are on the cusp of going public or achieving a significant milestone such as an acquisition.
5. Corporate Venture Capital (CVC):
Corporate venture capital involves investment from established corporations rather than independent venture capital firms. This form of investment allows corporations to gain exposure to innovative technologies and ideas.
The Impact
Venture Capital plays a crucial role in shaping the entrepreneurial landscape and driving innovation. Here’s how its impact resonates across various dimensions:
1. Fostering Innovation:
Venture Capital provides the fuel for innovation by supporting startups with groundbreaking ideas. This injection of capital allows entrepreneurs to bring their visions to life.
2. Job Creation:
The startups funded by venture capital often experience rapid growth, leading to job creation. This not only contributes to economic development but also fosters a culture of entrepreneurship.
3. Industry Disruption:
Many disruptive technologies and business models that have reshaped industries received initial funding and support from venture capitalists. This disruption often leads to improved efficiency and new market dynamics.
4. Economic Growth:
The success of venture-backed startups contributes significantly to economic growth. These companies not only create jobs but also generate tax revenue and contribute to overall economic prosperity.
5. Bridging Gaps in Funding:
Venture Capital fills the gap in funding that often exists for startups. Traditional lenders may be hesitant to invest in high-risk, unproven ventures, making venture capital a crucial bridge for these early-stage companies.
Challenges and Considerations
While Venture Capital is a powerful catalyst for growth, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
1. High Risk, High Reward:
The high-risk nature of venture capital investments means that not all startups will succeed. Investors must carefully assess the risk-return profile and diversify their portfolios.
2. Long Investment Horizon:
Investments typically have a longer time horizon before realizing returns. Investors need patience and a strategic approach to managing their portfolios.
3. Valuation Challenges:
Valuing early-stage startups can be challenging, and disagreements on valuation can arise during negotiations between investors and founders.
4. Limited Liquidity:
Investments often lack liquidity, meaning that investors may need to wait until an exit event, such as an IPO or acquisition, to realize returns.
5. Market Fluctuations:
Economic downturns or shifts in market conditions can impact the success of startups and the returns generated by venture capital investments.
Future Trends
As the venture capital landscape evolves, several trends are shaping the future of this dynamic industry:
1. Increased Diversity and Inclusion:
There is a growing emphasis on increasing diversity and inclusion within the venture capital ecosystem. Efforts are being made to support and fund startups led by women and underrepresented minorities.
2. Impact Investing:
It is increasingly aligning with social and environmental impact goals. Impact investing focuses on funding companies that generate positive social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns.
3. Rise of Angel Investors:
Angel investors, individuals who provide capital to startups in exchange for equity, are playing an increasingly prominent role in early-stage funding, complementing traditional venture capital.
4. Continued Technology Focus:
The technology sector continues to attract a significant share of venture capital investments, with a focus on areas such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and clean energy.
5. Globalization:
It is becoming more global, with investors and startups transcending geographical boundaries. This globalization opens up new opportunities and challenges for the industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Venture Capital stands at the forefront of fostering innovation, driving economic growth, and shaping the future of industries.
Its role in supporting startups with high growth potential is instrumental in creating a dynamic and thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem.
While challenges exist, the impact of successful venture capital investments extends far beyond financial returns, contributing to job creation, industry disruption, and societal progress.
Welcome all of you to my website. I keep updating posts related to blogging, online earning and other categories. Here you will get to read very good posts. From where you can increase a lot of knowledge. You can connect with us through our website and social media. Thank you