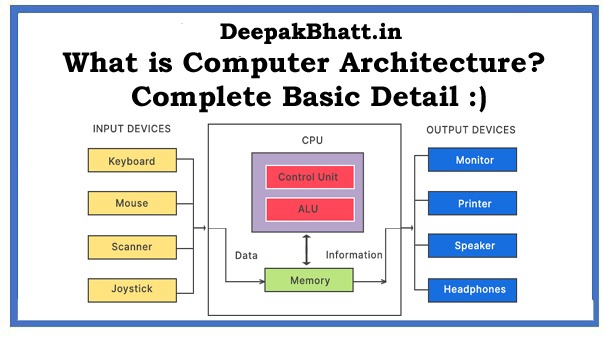
What is Computer Architecture Architecture can be concerned with this.
How the Control Processing Unit works. and how its user uses computer memory. There is some learning model.
With this, if you have a computer related to What is a Computer? If you do not know about Computer Operating Systems and Computer Software, then definitely read it once.
How to Create a Simple Business Plan
5 Books Will Make You a Better Entrepreneur
Computer Architecture
A microcomputer is one such computer built around a microcontroller model called the MicroStamp. Which has been integrated into a very large-scale integrated circuit.
It is a digital computer divided into CPU memory and input-output units. This is all subsystem communication over a single CPU bus.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
It is known as a processor or microprocessor. Is short for Central Processing Unit.
The CPU is responsible for handling all the instructions and calculations received from other hard drives. Where the components in the computer and the software programs running on the computer perform the legitimate processing of CPU data.
The processing of data is received from the main memory by the system bus. The result from the CPU is then sent back to the main memory.
Apart from the computer station, the CPU controls proper operation through system buses. The order and coordinates are divided into three major classes of principal components.
1. Control Unit
Controlling the receipt of instructions from the main memory and the subsequent execution of the instruction among all the operations performed including the control of input and output devices and the passing of data to the automatic logical unit for computation.
2. Arithmetic and Logical Unit
An arithmetic logic unit is part of a computer processor. Which performs automatic and logical operations on computer instructions operating in some processors.
The arithmetic logical unit is divided into two units the arithmetic unit and the logic unit. Some procedures have more than one thematic example, Unit 1 for fixed-point operations and another for floating-point operations.
3. Register Unit
A computer architecture or register consists of a small amount of storage available as a part of a digital processor. As the CPU they accept the data. The data is stored. And the data is transferred.
BUS
There is simply a communication system in computer architecture. Which transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers.
This expression includes all related hardware and software, including communication protocols. Computer buses were parallel electrical wires having many connections but the term is now used for any physical. An arrangement that provides some logical functionality in the form of parallel electric buses.
1. Control BUS
A computer bus is part of a computer. Which was used by the CPU to communicate with other devices within the computer. The control bus is used to take commands from the CPU and the return status signal from the device.
2. DATA BUS
The data bus carries the actual data. A bus that moves award to or from memory is called a data bus.
3. Address BUS
An address bus age of a computer bus is used to specify a physical address. Which is the specific memory location on the address bus.
CPU Machine Cycle
Each computer has a CPU. Which may have different cycles based on different instruction sets.
1. Receiving Instructions
The next instruction is obtained from the memory address. Which is currently stored in the program counter. The instruction is stored in the register.
2. Decode Instruction
The decode interprets the instruction during this cycle. In the case of memory instructions, the instruction inside gets decoded. The execution phase will occur in the next clock pulse.
3. Execute Instructions
The control unit of the CPU pulses the decoded information in the form of a sequence of control signals to the corresponding functional unit of the CPU to perform the necessary action.
Integrated Circuit IC
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on a small plate of semiconductor material. In general, silicon ICs can be made very compact. Servers are billions of transistors and other electronic components. In which there are several billion transistors. Each electronic circuit is called Byte.
A cell can be represented in 0 or 1 beat. Which depends on the flow of current in that call. Or the following ICs are used today in virtual or electronic devices.
and has revolutionized the world of electronics. Various generalizations of semiconductor techniques are used to follow.
1. Small-Scale Integration
The first integrated circuit with few transistors would have a cheaper one. In which a hundred components are made in a single chip.
2. Medium-scale integration
The next step in the development of ICs was taken in the late 1960s. Introduced a device consisting of a thousand transistors in two single chips. Each ship was called an MLI.
3. Very Large Scale Integration
The development driven by a single economic factory led to large-scale integration in the mid-1970s. In which 30000 transistors were in single-chip.
4. Very Large Scale Integration
Development started with 1 million or more transistors.
5. Ultra Large Scale Integration
Short for Ultra Large Scale Integration, ULIC is an IC. Which has more than 3 million components cheaply.
Factors Affecting CPU Speed
1. Instruction Set
It is the processor built into the code that does this. That’s how to perform its duties as it is built into the CPU. And it’s nothing like that. which you can change. or update.
2. Clock Speed
The clock speed starts in MHz or GHz. The faster the clock processor can complete the more instructions per second.
3. Bandwidth
Determines bandwidth. How much information can the processor process in one instruction? If you compare the data flow to the traffic flow or highway then the clock speed will be the speed limit. And the bandwidth will be the number of lenses on the highway. Current bandwidth is the standard 64-bit for desktop and laptop PCs. And 32-bit is official or a thing of the past.
4. Font Size
Font size limits that rate. On which the data can get to the CPU. Which in turn limits that rate. At which the CPU can process that data at the speed of the CPU. on which it can transfer the data to the rest of the system.
Some FAQ
1. What is the basic structure of a computer?
Talk about the basic structure of a computer. So hardware, software, processor, storage, etc. are the components of its structure.
2. What are the components of computer architecture?
Computer Architecture Components CPU, Input, Output, Storage, etc. It’s a component.
Conclusion
Basic information about computer architecture has been given to you in this post. You are going to get more information in the coming new post.
In this post, we got information about the component integrated circuit of the CPU and complete basic information has been given in this post.
Hope you liked this post and got complete information about Computer Architecture. If you got to learn something in the post, then definitely share it with your friends.
Welcome all of you to my website. I keep updating posts related to blogging, online earning and other categories. Here you will get to read very good posts. From where you can increase a lot of knowledge. You can connect with us through our website and social media. Thank you